Vein-related health issues are common, particularly among adults, and two of the most frequently discussed conditions are deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and varicose veins (VV). Although both affect the veins in your legs, they differ significantly in terms of severity, causes, symptoms, and treatment options. While varicose veins are often seen as a cosmetic concern, deep vein thrombosis is a potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate attention. Understanding these conditions and knowing when to seek medical help is vital for maintaining healthy veins and preventing complications.
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep vein thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the lower leg or thigh. This condition arises when blood flow slows down, causing blood to clot and form a blockage in one of the deep veins. Although it might not be immediately noticeable, DVT can lead to serious health issues if left untreated.
One of the most dangerous aspects of DVT is that the clot can break loose and travel through the bloodstream, potentially lodging in the lungs, leading to a pulmonary embolism (PE)—a life-threatening condition. Approximately 900,000 Americans experience venous thromboembolisms each year, which includes both DVT and pulmonary embolism.
Common Risk Factors for DVT:
- Prolonged immobility (e.g., long flights, extended bed rest)
- Recent surgery, particularly orthopedic or abdominal procedures
- Certain medications, such as birth control pills or hormone therapy
- Genetic factors, such as a history of blood clotting disorders
- Being overweight or obese
Symptoms of DVT:
- Swelling in one leg (often more noticeable than the other)
- Pain or tenderness in the affected leg, especially when standing or walking
- Warmth in the affected area
- Red or discolored skin over the affected vein
If left untreated, DVT can lead to long-term complications like post-thrombotic syndrome, which causes chronic pain, swelling, and skin changes in the affected leg. If you notice symptoms of DVT, it’s essential to seek medical care right away to avoid serious complications.
What are Varicose Veins?
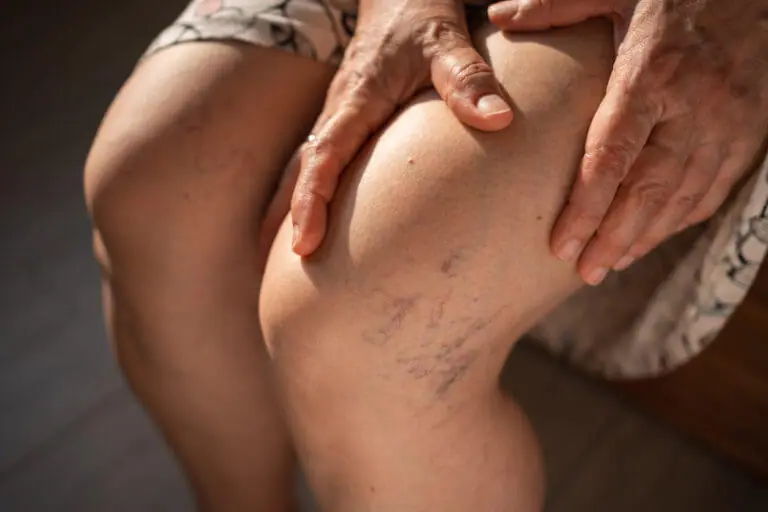
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that are visible just beneath the skin’s surface, primarily in the legs. They develop when the valves within the veins weaken or become damaged, causing blood to pool and the veins to bulge. While varicose veins are often seen as a cosmetic issue, they can cause discomfort, aching, and even lead to more severe conditions if not addressed.
Unlike DVT, varicose veins are not typically life-threatening, but they can affect the quality of life, especially when they become painful or cause swelling. Varicose veins tend to be more visible and can create a feeling of heaviness in the legs.
Common Causes and Risk Factors for Varicose Veins:
- Age (older adults are more likely to develop them)
- Pregnancy (due to hormonal changes and increased blood volume)
- Obesity (excess weight puts pressure on the veins)
- Prolonged standing or sitting (common in jobs that require long hours of standing)
- Genetics (family history of varicose veins)
Symptoms of Varicose Veins:
- Swollen, twisted veins that may appear blue, red, or purple
- Aching or heavy legs, particularly after standing for long periods
- Itchiness or dryness around the affected veins
- Skin discoloration and sores near the veins, in severe cases
While varicose veins are generally not life-threatening, they can cause significant discomfort and lead to more serious issues like skin ulcers, blood clots, or excessive bleeding in the affected veins.
Key Differences Between DVT and Varicose Veins
Although both conditions affect the veins, their causes, symptoms, and potential complications vary significantly:
| Aspect | Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) | Varicose Veins (VV) |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Blood clot forms in a deep vein | Weak or damaged valves cause blood pooling in veins |
| Severity | Can be life-threatening if untreated | Generally not life-threatening, but can be painful |
| Symptoms | Swelling, pain, warmth, redness in one leg | Swollen, twisted veins; aching, heaviness in legs |
| Potential Complications | Pulmonary embolism, post-thrombotic syndrome | Skin ulcers, bleeding, chronic pain |
| Treatment | Anticoagulants (blood thinners), compression stockings, surgery (IVC filter) | Sclerotherapy, laser treatment, compression stockings |
Treatment Approaches for DVT
The primary goal in treating DVT is to prevent the clot from growing, breaking loose, and traveling to the lungs. Treatment options include:
- Anticoagulants (Blood Thinners): These medications prevent further clotting and help reduce the risk of the clot traveling to the lungs. The duration of anticoagulant therapy varies depending on the severity of the clot.
- Compression Stockings: These stockings improve circulation in the legs, reducing swelling and pain.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise and elevating the legs can improve blood flow.
- Surgical Treatments: In some cases, doctors may use a filter (inferior vena cava filter) to catch any clots that break free before they can reach the lungs.
Treatment Approaches for Varicose Veins
For varicose veins, the focus is on relieving symptoms and preventing further vein damage:
- Compression Stockings: These stockings help reduce swelling and prevent blood from pooling in the veins.
- Sclerotherapy: This involves injecting a solution into the vein, causing it to collapse and fade over time.
- Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT): A laser is used to heat and close off the affected vein.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Similar to EVLT, this treatment uses radiofrequency energy to close off the problematic vein.
When to Seek Help
Both DVT and varicose veins require medical attention, but DVT is a much more urgent condition due to its life-threatening risks. If you experience swelling, pain, or redness in one leg, especially after being immobile for a long time, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention.
On the other hand, while varicose veins are rarely dangerous, they can still cause significant discomfort and lead to complications over time. If your varicose veins are causing persistent pain, swelling, or other symptoms, consulting a vein specialist can help prevent worsening conditions and improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between deep vein thrombosis and varicose veins is crucial for recognizing the appropriate symptoms and seeking the right treatment. While varicose veins may be more common and less severe, DVT requires prompt medical intervention to prevent serious complications. If you’re experiencing symptoms of either condition, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your needs. Proper care can help you maintain healthy veins and lead an active, comfortable life.